生薬学分野 Pharmacognosy
-
教授 Professor
森元 聡 [博士(薬学)] Satoshi Morimoto, Ph.D.
-
准教授 Associate professor
田中 宏幸 [博士(薬学)] Hiroyuki Tanaka, Ph.D.
-
助教 Research Assistant
坂元 政一 [博士(薬学)] Seiichi Sakamoto, Ph.D.
大麻成分の生合成に関する研究
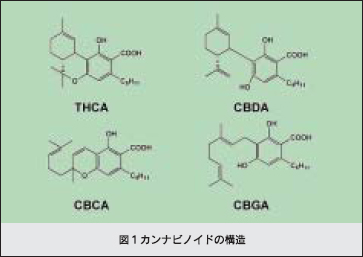 大麻の基原植物であるアサは、カンナビノイドとよばれるユニークな二次代謝産物を生産しています(図1)。当研究室では、各種カンナビノイドの生合成酵素に関する研究を行っており、これまで、THCA,CBDA及びCBCAの生合成を触媒する酵素の精製やそれらの遺伝子クローニングに成功しています。また、さらに上流の生合成ステップを触媒する酵素群の遺伝子のクローニングも完了しています。現在、カンナビノイド合成酵素のX線結晶解析を試みており、THCA合成酵素に関しては、立体構造の解明に成功しています。このデータをもとに原子レベルでTHCA合成酵素反応のメカニズムを明らかにすることも検討しております。
大麻の基原植物であるアサは、カンナビノイドとよばれるユニークな二次代謝産物を生産しています(図1)。当研究室では、各種カンナビノイドの生合成酵素に関する研究を行っており、これまで、THCA,CBDA及びCBCAの生合成を触媒する酵素の精製やそれらの遺伝子クローニングに成功しています。また、さらに上流の生合成ステップを触媒する酵素群の遺伝子のクローニングも完了しています。現在、カンナビノイド合成酵素のX線結晶解析を試みており、THCA合成酵素に関しては、立体構造の解明に成功しています。このデータをもとに原子レベルでTHCA合成酵素反応のメカニズムを明らかにすることも検討しております。
植物の生体防御システムに関する研究
 ケシ(図2)に含まれるモルヒネは鎮痛剤として末期がん患者の疼痛治療に使われています。モルヒネはアルカロイドとしては最初に単離された植物成分ですが、なぜケシがこのような化合物を生産しているのか、全く判っていませんでした。そこでモルヒネの代謝系を調べたところ、ケシが傷害を受けるとモルヒネが二量化し、そのものがペクチンに結合して細胞壁を強化し、細胞を守ることを解明しました。
ケシ(図2)に含まれるモルヒネは鎮痛剤として末期がん患者の疼痛治療に使われています。モルヒネはアルカロイドとしては最初に単離された植物成分ですが、なぜケシがこのような化合物を生産しているのか、全く判っていませんでした。そこでモルヒネの代謝系を調べたところ、ケシが傷害を受けるとモルヒネが二量化し、そのものがペクチンに結合して細胞壁を強化し、細胞を守ることを解明しました。
植物の細胞死に関する研究
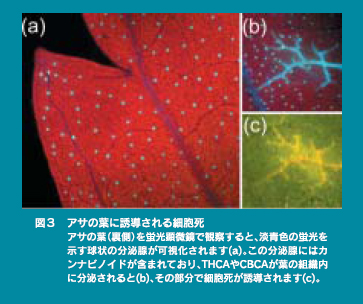 植物の細胞死は、様々な重要な生体反応(老化、分化や病原微生物に対する生体防御反応など)に関与することが知られています。いろいろな植物の細胞死の誘導メカニズムを調べたところ、アサでは内在性成分のTHCAやCBCAが葉にネクローシス型の細胞死を誘導することを発見しました。
植物の細胞死は、様々な重要な生体反応(老化、分化や病原微生物に対する生体防御反応など)に関与することが知られています。いろいろな植物の細胞死の誘導メカニズムを調べたところ、アサでは内在性成分のTHCAやCBCAが葉にネクローシス型の細胞死を誘導することを発見しました。
Research
-
- Three enzymes (THCA-, CBDA-, CBCA-synthases) which catalyze biosynthesis of marihuana compounds (cannabinoides) were purified from Cannabis leaves, and their enzymatic properties were extensively investigated in our laboratory. We have now attempted molecular cloning, expression and crystallization of these synthases. Among them, we succeed in determination of the crystal structure of THCA synthase, and based on these data, the mechanism of THCA-synthase reaction has been examined.
- We found that morphine is metabolized to bismorphine in response to stress in opium poppy. This bismorphine specifically binds to pectin in the cell wall of opium poppy, resulting in resistance to hydrolysis by pectinase.
- Cell death in higher plant is known to be involved in a variety of physiological events such as senescence and defense against microbial pathogens. When cell death-inducing mechanism in several plants was examined, we discovered that cannabinoids induce necrotic cell death in Cannabis leaves. Although why Cannabis sativa produces cannabinoids have not been unclear, thus we could reveal their physiological functions in host plant.
代表論文
-
- S. Morimoto et al., Cannabinoids act as endogenous cell death regulators that mediate mitochondrial permeability transition in Cannabis sativa (hemp)(2007), J. Biol. Chem., 282, 20739-20751.
- Y. Shoyama et al., Crystallization of THCA synthase from Cannabis sativa (2005), Acta Crystal. (F) 61, 799-801.
- S.Sirikantaramas et al., The gene controlling marijuana psychoactivity molecular cloning and heterologous expression of THCA from Cannabis sativa (2004), J. Biol. Chem., 279, 39767-39774
- S. Morimoto et al., Morphine metabolism in the opium poppy and its possible physiological function (2001), J.Biol.Chem., 276, 38179-38184.
- K. Sasaki et al., Molecular characterization of a novel β-glucuronidase from Scutellaria baicalensis Georgi (2000), J.Biol.Chem., 275, 27466-27472.
分野連絡先
-
森元 聡(Satoshi Morimoto)
- TEL:
-
FAX:
092-642-6580
-
E-mail:
morimoto★phar.kyushu-u.ac.jp
(メールアドレスは★を@と置き換えてください。)